Summary
- Layer 3 blockchains build on Layer 1 and Layer 2 to offer customized, application-specific solutions, enhancing DApp functionality and scalability.
- A defining feature of L3 blockchains is their ability to facilitate seamless communication between different blockchains. Through advanced cross-chain communication protocols, layer 3s enable smooth interactions between decentralized applications across various blockchain networks.
- Layer 3 blockchains leverage off-chain computation and innovative consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake (PoS) to achieve greater scalability and efficiency.
- A version of this article first appeared on Cointelegraph. Read more Crypto Council Explainers.
Layer 3 Blockchains
Layer 3 blockchains refer to a layer of blockchain technology built on top of base layers to provide customized application-specific blockchains tailored to users’ needs. Created on the foundations of layer-1 and layer-2 solutions, layer 3 blockchains offer improved functionality for decentralized applications (DApps), marking a new chapter in the development of blockchain technology. By providing users with a more flexible, effective and user-friendly blockchain ecosystem, L3 blockchains aim to overcome the limitations of L1s and L2s and accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology.
L3s primarily focus on linking different blockchains, enabling them to communicate smoothly. Layer 3s are designed to offer more comprehensive solutions for scaling, performance, interoperability, customized functionality, security and cost. The main characteristics of L3 blockchain technology are enhanced transaction throughput, cross-chain communication protocols and smart contract capability, which facilitate intricate DApps and network interactions. In addition, layer-3 blockchains frequently integrate advanced governance mechanisms to ensure efficient decision-making and protocol evolution.
Source: Cointelegraph
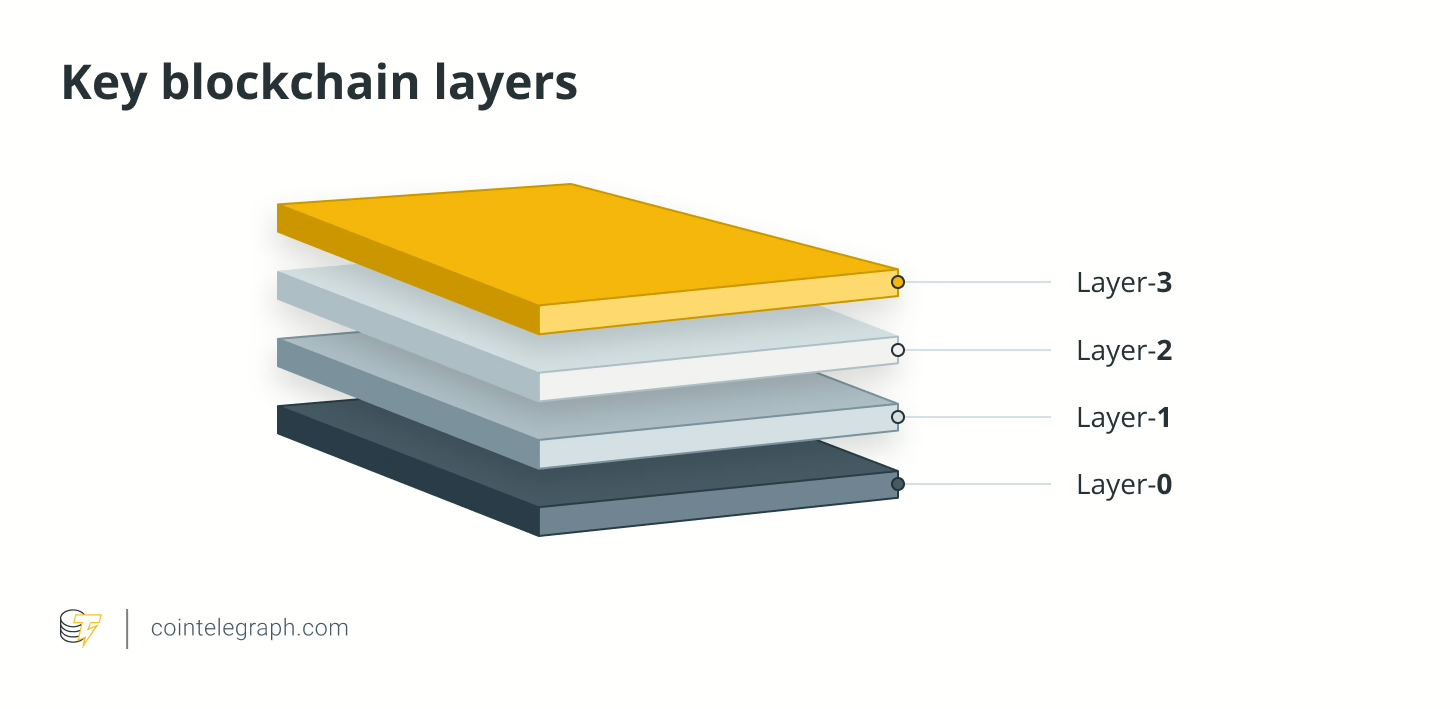
Blockchain Layers Overview
Blockchain technology can be described as multilevel building, with L1 reflecting the fundamental architecture, L2 adding functionalities and L3 powering applications. The consensus mechanism, scalability solutions, transaction speed and security features of each layer vary.
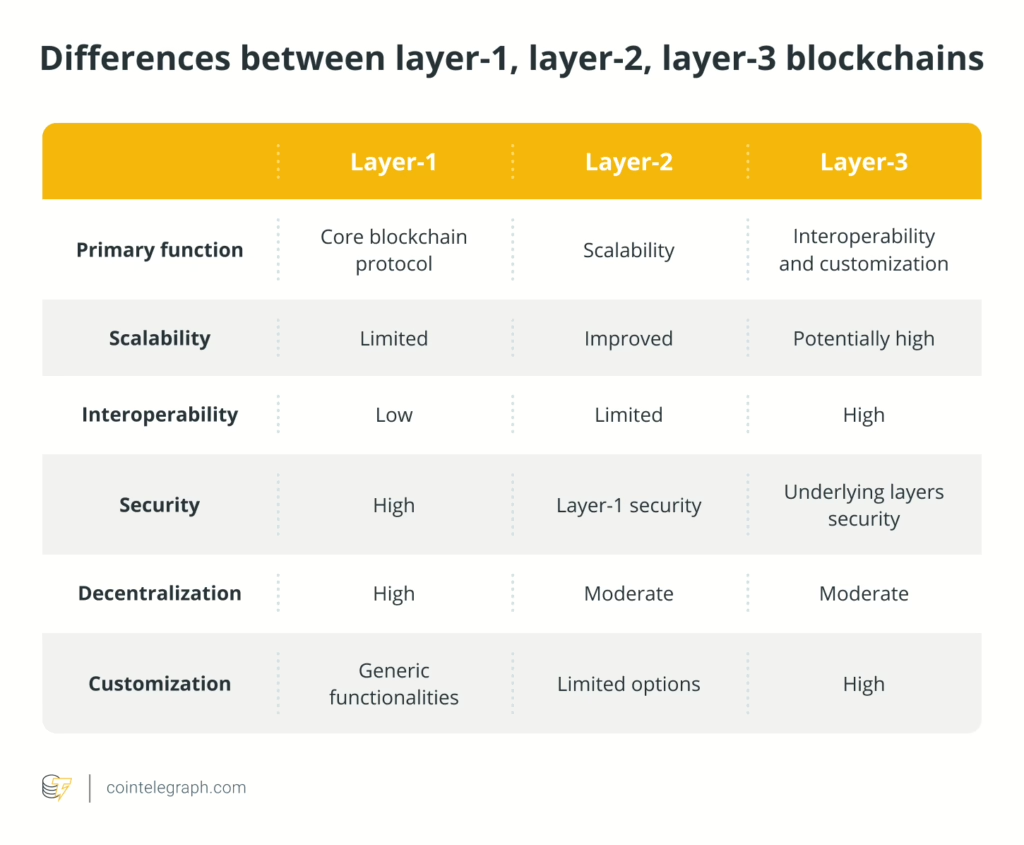
Layer 1 (base layer)
Layer-1 blockchains are where the blocks are added, and the transactions are finalized, providing a secure foundation for a blockchain network. These decentralized networks rely on consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake (PoS) for transaction validation. Layer-1 blockchains are independent of any other network.
L1s ensure security and validate transactions but are often overwhelmed by high volumes of transactions. L1 blockchains also suffer from the blockchain trilemma, which refers to the trade-off between blockchain scalability, decentralization and security to achieve optimal performance and functionality.
Layer 2 (built on base)
Built on the foundations of layer 1, layer-2 blockchain solutions are secondary protocols that improve the functionality of the base layer without functioning as separate blockchains. These L2 solutions, which can be state channels, rollups and sidechains, are designed to alleviate the scalability issues with layer-1 blockchains.
Through off-chain computation and periodically settling the transactions on the main chain, layer 2s achieves a higher transaction speed and reduced costs without compromising on security. Nevertheless, while L2s noticeably improve scalability, they may be limited by blockchain interoperability and customization issues.
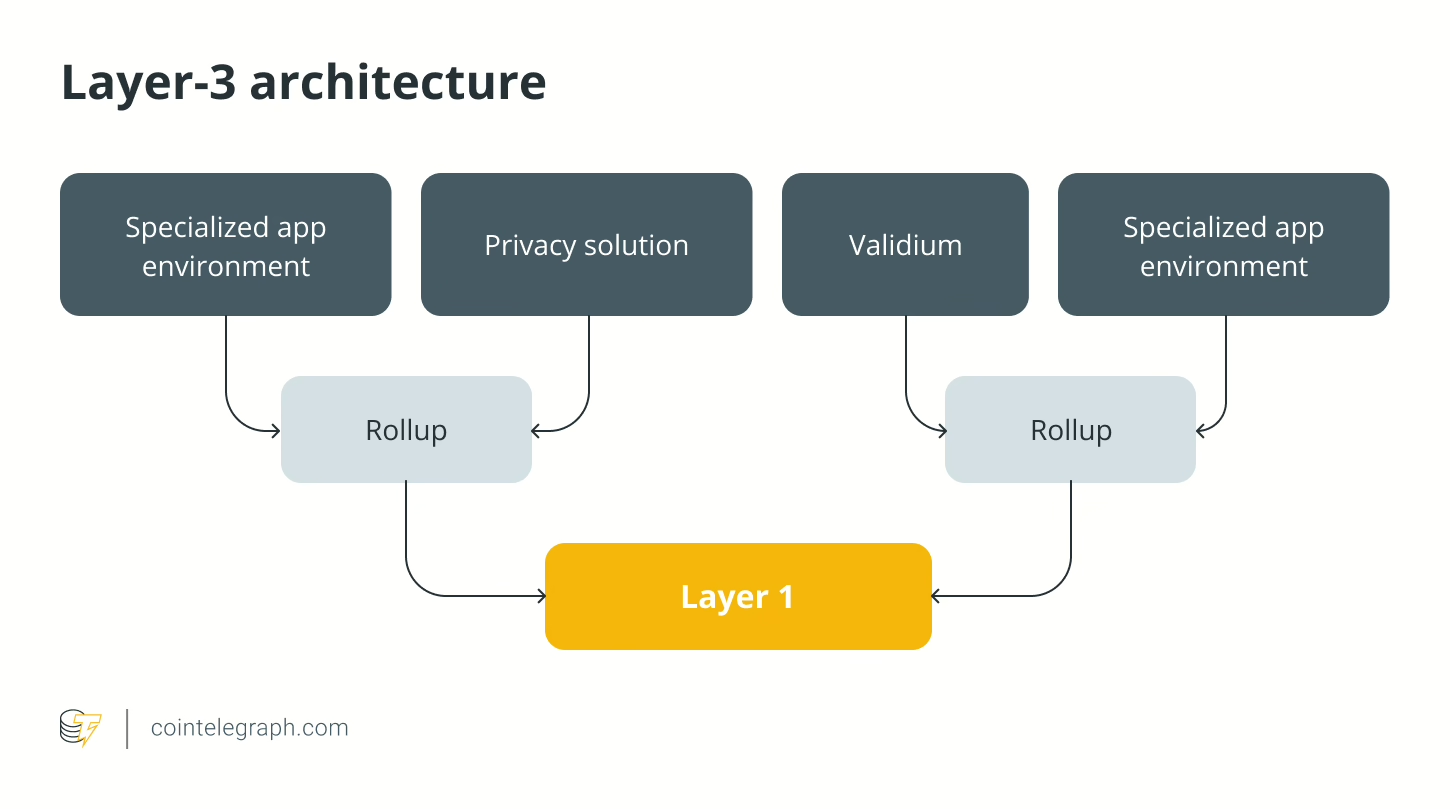
Layer 3 (application layer)
Layer-3 blockchains act as an application layer, leveraging the functions of base layers. They enhance scalability beyond L2s, enabling higher transaction throughput and tailored applications. Layer 3s foster efficient and cost-effective financial transactions through scalability and a blend of layered consensus algorithms such as PoS and proof-of-authority, ensuring network performance, decentralization and security.
L3s distinctive feature is facilitating seamless communication and interoperability among various blockchain networks without intermediaries. With advanced protocols and cross-chain bridges, layer 3s unlock opportunities in decentralized finance (DeFi), asset tokenization and cross-border payments.
Source: Cointelegraph
How Layer 3 Blockchains Work
Layer-3 blockchains leverage off-chain computation and novel consensus mechanisms to achieve scalability and interoperability for decentralized applications. Layer-3 blockchains leverage the security and transactional capabilities of L1s and L2s, adding more sophisticated smart contract features.
Layer-2 scaling solutions, such as state channels and sidechains, allowed layer 3s to perform complex off-chain computation and settlement while maintaining the underlying blockchain’s security and high performance. Layer 3s enhance interoperability by enabling communication between different blockchains through protocols like the inter-blockchain communication (IBC). This also provides smooth communication between different DApps, including DeFi and the nonfungible tokens (NFTs) developed on different blockchains.
Virtual machine environments, which are specialized within L3 architecture, provide the ground for the execution of multiple DApps through the deployment of smart contracts. These environments enable the execution of arbitrary code on the blockchain, allowing the developers to create DApps with advanced functionalities.
Rollups are another critical component of layer 3s that optimize transaction throughput by grouping multiple transactions into a single compressed data structure. By batching the transactions off-chain and periodically committing them to layer 1, rollups improve scalability without sacrificing security.
Layer-3 protocols frequently implement innovative consensus mechanisms such as PoS or delegated proof-of-stake. These consensus algorithms improve the network’s scalability and energy efficiency while preserving the system’s decentralization and security, enhancing the capabilities of layer-3 blockchains.
Source: Cointelegraph